What Are Liabilities in Accounting?
Consider prepaid insurance, where a company pays a premium for 12 months of coverage upfront, creating a “prepaid insurance” asset. Each month, a portion of this asset is moved to “insurance expense” on the income statement as the coverage is used. In the following month, when updating the vacation accrual, you would only record the […]
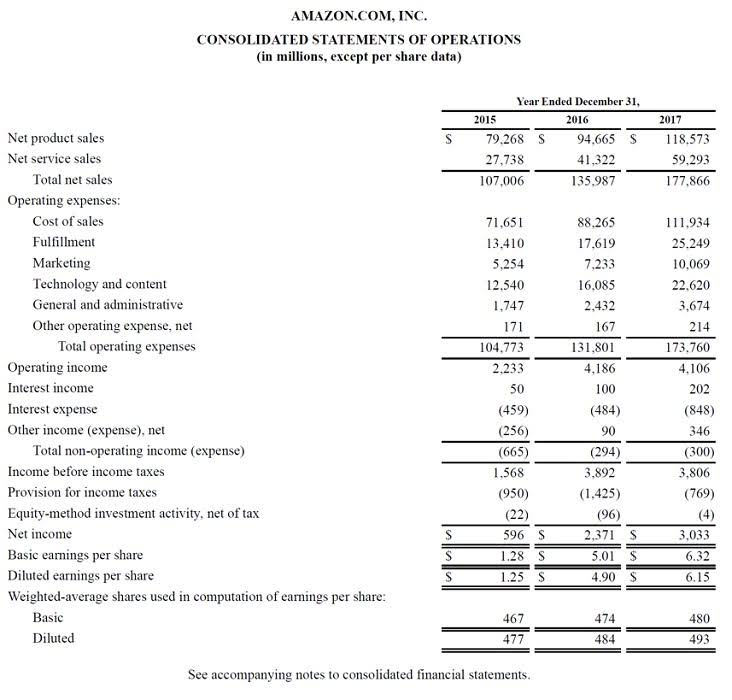
Consider prepaid insurance, where a company pays a premium for 12 months of coverage upfront, creating a “prepaid insurance” asset. Each month, a portion of this asset is moved to “insurance expense” on the income statement as the coverage is used. In the following month, when updating the vacation accrual, you would only record the difference between the current month’s balance and the previous month’s balance. This ensures that the liability is accurately reflected on the balance sheet without double-counting the expense.

Bull Terrier vs. Pit Bull: Key Differences in Terrier Breeds

By analyzing these concepts, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into a company’s financial performance, its ability to meet its obligations, and its overall financial health. Distinguishing between liabilities and expenses can trip up even experienced finance teams. These classification errors don’t just affect your books—they can lead to cash flow surprises, compliance issues, and poor business decisions based on inaccurate data.
Examples:
- They go to the shareholders or sell the bonds to individuals to pump in more money.
- The actual purchase of the equipment is an expense, and over time, the equipment depreciates, which is also an expense on the income statement.
- Sage makes no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness or accuracy of this article and related content.
- It is best to envision the company balance sheet when analyzing the relevant accounting entry process.
- Did it create an obligation, meaning a future cost that the company will owe?
To master the art of financial wizardry, companies must accurately recognize and measure their expenses. By doing so, they can determine their true cost of doing business and make informed decisions to improve profitability. Liabilities come in all difference between liabilities and expenses shapes and sizes, from short-term loans to long-term bonds. They’re like the villains of the financial world, lurking on the balance sheet and waiting to be defeated by timely payments.

Term Deposit vs. Fixed Deposit: Key Differences in…
- This treatment can defer tax benefits, as the costs are amortized over the benefit period.
- For example, if you pay cash for office supplies, debit the “Office Supplies Expense” and credit “Cash.” This practice ensures your income statement reflects all business costs accurately.
- Companies should balance short-term financial advantages with long-term strategic goals.
- A good accountant or bookkeeper will work with you to ensure your financial records are accurate.
- Because contingent liabilities are recorded depending on future events, they look more like potential liabilities.
- In this Accounting Basics tutorial I discuss the five account types in the Chart of Accounts.
Financial experts emphasize the importance of understanding the distinction between liabilities and expenses. Properly classifying and managing both is essential for maintaining financial stability and achieving sustainable growth. Misclassifying an https://www.bookstime.com/ expense as a liability, or vice versa, can distort financial reports and lead to inaccurate assessments of a company’s performance. As the company consumes the benefits, the expense is allocated to the corresponding periods through adjusting journal entries.

When a business purchases goods or services on credit, the supplier issues a bill detailing the items, HOA Accounting quantity, unit price, total amount due, and payment terms. This document becomes evidence of the transaction and forms the basis for recording the liability in accounting records. Payroll liability indicates a company owes money to employees for wages. Each week, however, the company incurs payroll expenses, such as the $800 weekly charge for employing the administrative assistant listed above. Companies can record a payroll liability each week by debiting payroll expense and crediting payroll liability.


